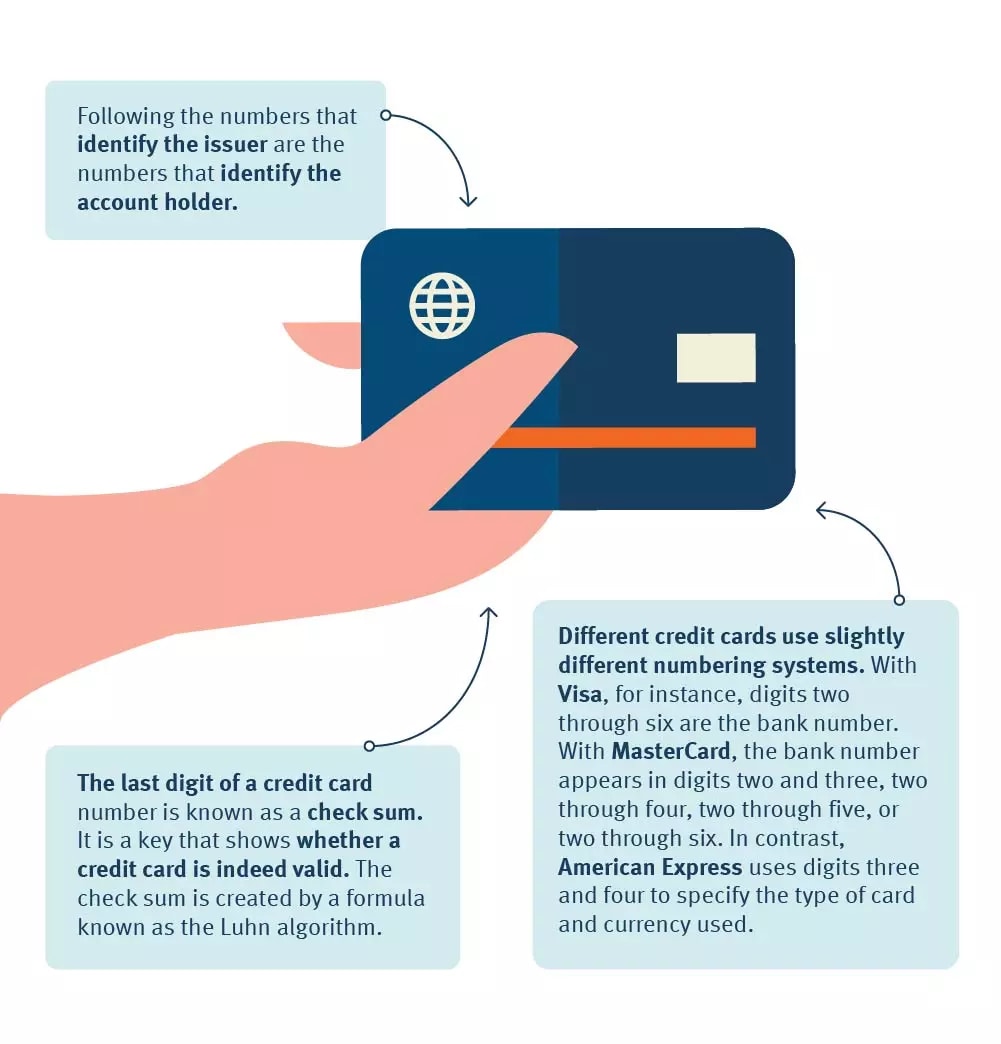
A credit card number is a long set of digits displayed across the front or back of your plastic or metal credit card. It’s typically 16 digits in length, often appearing in sets of four, and it’s used to identify both the credit card issuer and the card itself.
Credit card numbers aren’t randomly assigned; they’re coded to identify the issuer, the network, the account, and the unique card, all in an effort to prevent theft and fraud. The credit card number must fit a complex pattern in order to work.